



As America takes steps to improve our energy security, home-grown fuel sources are more important that ever. One of the fuel sources of the future is algae, small aquatic organisms that convert sunlight into energy and store it in the form of oil. Scientists and engineers at the Energy Department and its national laboratories are researching the best strains of algae and developing the most efficient farming practices. This edition of Energy 101 shows how oil is extracted from algae and refined into sustainable biofuels.

See how marine and hydrokinetic technologies harness the energy of the ocean's waves, tides, and currents and convert it into electricity to power our homes, buildings and cities.

See how organic materials like corn stover, wheat straw, and woody plants are being used to create homegrown biofuels in the United States—all while reducing our dependence on foreign oil and creating jobs in rural America.
See how we can generate clean, renewable energy from hot water sources deep beneath the Earth's surface. The video highlights the basic principles at work in geothermal energy production, and illustrates three different ways the Earth's heat can be converted into electricity.

You may already know that public transportation reduces pollution and eases congestion on the road. However, many transit fleets are switching over to cleaner, alternative fuels and technologies, making this mode of transportation even more sustainable. Watch this video for examples of these clean fleets, in our busy urban centers and our peaceful national parks.

The following edit was recommended by DOE's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy's Geothermal Technologies Office: At :58, “During the winter, the air is usually cooler than the temperature below ground. The solution circulates in a loop underground and absorbs the Earth's heat. This heat is brought to the surface and transferred to a heat pump. T̶h̶e̶ ̶h̶e̶a̶t̶ ̶p̶u̶m̶p̶ ̶w̶a̶r̶m̶s̶ ̶t̶h̶e̶ ̶a̶i̶r̶ ̶a̶n̶d̶ ̶y̶o̶u̶r̶ ̶r̶e̶g̶u̶l̶a̶r̶ ̶h̶e̶a̶t̶i̶n̶g̶ ̶s̶y̶s̶t̶e̶m̶ ̶w̶a̶r̶m̶s̶ ̶t̶h̶e̶ ̶a̶i̶r̶ ̶s̶o̶m̶e̶ ̶m̶o̶r̶e̶ ̶t̶o̶ ̶a̶ ̶c̶o̶m̶f̶o̶r̶t̶a̶b̶l̶e̶ ̶t̶e̶m̶p̶e̶r̶a̶t̶u̶r̶e̶.̶ ̶F̶i̶n̶a̶l̶l̶y̶ Ducts circulate the air to the various rooms.” --- An energy-efficient heating and cooling alternative, the geothermal heat pump system moves heat from the ground to a building (or from a building to the ground) through a series of flexible pipe "loops" containing water.

Biomass is an organic renewable energy source that includes materials such as agriculture and forest residues, energy crops, and algae. Scientists and engineers at the U.S. Department of Energy and its national laboratories are finding new, more efficient ways to convert biomass into biofuels that can take the place of conventional fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. This edition of Energy 101 shows how biomass is broken down and refined into sustainable biofuels via biochemical and thermochemical processes.

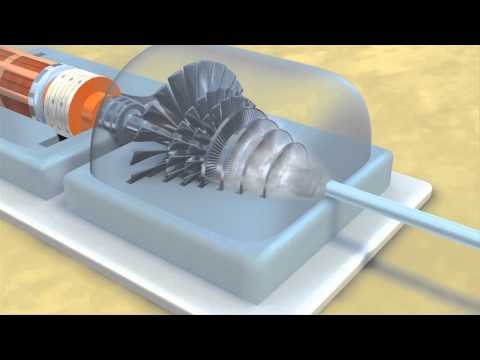
See how wind turbines generate clean electricity from the power of the wind. Highlighted are the various parts and mechanisms of a modern wind turbine.

Learn how hydropower captures energy from moving water and turns it into electricity for our homes and businesses.

Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems can generate clean, cost-effective power anywhere the sun shines. This video shows how a PV panel converts the energy of the sun into renewable electricity to power homes and businesses.